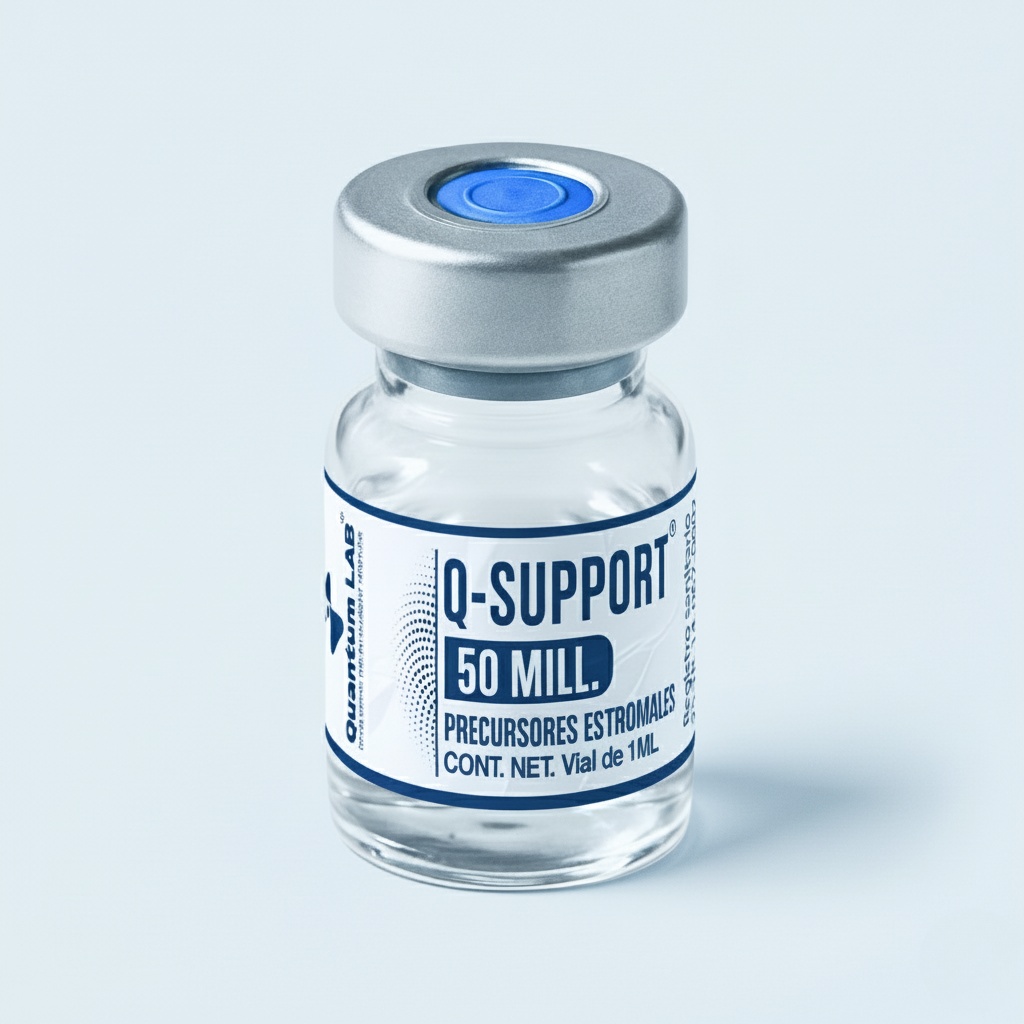
Stromal Precursors (MSC)
Cell population characterized according to ISCT criteria. Use as therapeutic adjunct in inflammatory control protocols and tissue repair support.
Presentation and concentration

Mechanism and evidence
Immunomodulation: adjustment of the immune microenvironment and cytokine profile (in vitro / in vivo).
Paracrine signaling: release of soluble factors and extracellular vesicles (exosomes) carrying mRNA/miRNA and proteins involved in tissue repair processes.
Trophic and angiogenic support: contribution to local cell survival and functional neovessel formation in injury environments.
Matrix remodeling: participation in the regulation of the extracellular matrix and associated remodeling and fibrosis processes.
Origin and method
Low insulation and expansion controlled conditions and standard operating procedures. Batches released with analytical specifications and documented traceability (see COA).
Characterization and quality
Identity (ISCT): CD73+/CD90+/CD105+; CD14–/CD19–/CD34–/CD45–/HLA-DR–.
Functionality: osteo/adipo/chondrogenic potential (when applicable).
Microbiological safety: sterility (USP), mycoplasma (qPCR) and endotoxins (LAL).
Viability and cell count: determined in release.
Acceptance criteria: within established specifications.
Use and preparation
Routes according to clinical evaluation: IV, intraarticular, intralesional, intrathecal (protocols).
Conservation and logistics
Storage: 2-8 °C in its original packaging.
Cold chain: do not administer if you have discontinued.
Post-shipment window: do not use if the following have elapsed > 72 h since leaving the laboratory.
Shelf life / post-dilution window: consult the COA in force.
What are mesenchymal stem cells (MSC)?
Also called mesenchymal stromal cells (ISCT terminology), are cells multipotent with the ability to differentiate in vitro into lineages with bone, cartilaginous and adipose. Isolated from bone marrow, adipose tissue y perinatal sources like placenta y Wharton's jelly.
Identity and key features
ISCT characterization: adhesion to plastic; CD73⁺/CD90⁺/CD105⁺/CD105⁺ y
CD14⁻/CD19⁻/CD34⁻/CD45⁻/HLA-DR⁻.Predominant mechanism: action paracrine through secretoma and extracellular vesicleswhich modulate inflammation y promote tissue repair.
Framework for clinical use: are used as adjuvant coadjuvant in specialist-indicated protocols (e.g., orthopedics, wound management, dermatology). Robust evidence is preclinical and early clinical seriesthe indication is case by case under medical criteria and current regulations.
Actual effective dose
Actual effective dose
The % of live cells defines how many cells are actually available per presentation and reduces adjustments during the procedure.
Documentation per lot
Cytometry results, cell counts, microbiological controls and identity parameters; integrates the necessary information for clinical decisions and audits.
Declared viability
Release threshold established by current specification; method and batch values are documented.
Inter-lot reproducibility
Control of viability and count variability to ensure consistent dosing and greater comparability of clinical results.
Our biotechnology products
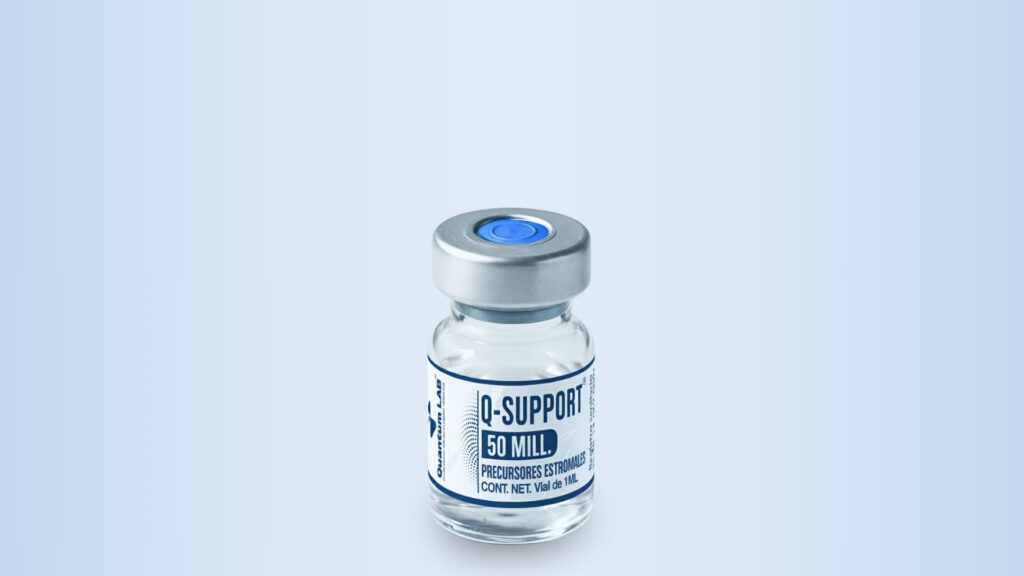

Stromal Precursors (MSC)
10 Million
25 Million
50 Million
Mechanism and evidence
Paracrine and immunomodulation: factors and EV that adjust inflammation and promote repair.
Odontogenic/bony potential: differentiation odontoblast-like and bone; better performance with scaffolding adequate.
Regenerative endodontics: evolving protocols; results heterogeneous between studies.
Periodontium/implants: support in intrabony defects and ridge preservation (early evidence).
Natural Killer (NK) Cells
25 Million
50 Million
Mechanism and evidence
Direct cytotoxicity: cell recognition with MHC-I low/absent and lysis by perforin/granzymes.
ADCC (CD16): synergy with monoclonal antibodiesdestroys cells opsonized with IgG.
Immunoregulation: secretion of IFN-γ/TNF-α y crosstalk with dendritic and Tadjusting the tumor microenvironment.
Evidence framework: mechanisms valid in basic immunology; ongoing clinical translationwith response influenced by patient status, KIR/HLA profile and degree of activation ex vivo.
Exosomes
1,550 µg per vial of 5 mL
Mechanism and evidence
They act as natural mediators of cellular communication, transferring proteins, RNA and bioactive factors that modulate the inflammatory response and stimulate endogenous regeneration mechanisms.
Promote the controlled angiogenesisthe reorganization of the extracellular matrix and the functional recovery of tissuereducing variability in clinical outcomes and return-to-work times.
Developed for scenarios where predictable recovery, pain reduction y sustained tissue stability during follow-up.
